HOUSTON JOURNAL OF
MATHEMATICS
Electronic Edition Vol. 51, No. 1, 2025
Editors: D. Bao (San Francisco, SFSU), S. Berhanu (Temple), D. Blecher
(Houston), B. G. Bodmann (Houston),
M. Gehrke (CNRS),
Y. Hattori (Matsue, Shimane), A. Haynes (Houston), W. B. Johnson (College Station), H. Koivusalo (Bristol),
T. H. Lê (Mississippi),
M. Marsh (Sacramento),
M. Ru (Houston), S. W. Semmes (Rice), D. Werner (FU Berlin).
Managing Editors: B. G. Bodmann and A. Haynes (Houston)
Houston Journal of Mathematics
Contents
Xiaoliang Cheng, College of Mathematics and Computer, Jilin Normal University, Siping,
136000, China(chengxiaoliang92@163.com), Kuai Yu, College of Mathematics and
Computer, Jilin Normal University, Siping, 136000, China(yk2761219361@gmail.com),
Lin Gui, College of Mathematics and Computer, Jilin Normal University, Siping,
136000, China(guilin7777777@163.com), and An Wang, School of Mathematical
Sciences, Capital Normal University, Beijing, 100048, China(wangan@cnu.edu.cn).
The Bergman kernel function and the vanishing theorem for Forelli-Rudin construction
on the classical domain of second class, pp. 1–29.
ABSTRACT. We investigate the d-boundedness of the Bergman kernel function for
Forelli-Rudin construction on the classical domain of second class. We derive
the Bergman kernel function using the series method and Hua’s method. In
particular, the finite form is derived through this approach. We also obtain that the
Bergman kernel function is d-bounded concerning the Bergman metric. Finally,
we prove that the L2-cohomology vanishing theorem on this domain is valid.
Asha Barua, School of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences, University of Texas
Rio Grande Valley, 1201 West University Drive, Edinburg, TX 78539-2999,
USA (ashabarua@vt.edu), Angelina Chavera, School of Mathematical and
Statistical Sciences, University of Texas Rio Grande Valley, 1201 West University
Drive, Edinburg, TX 78539-2999, USA (angelinachavera1@gmail.com), Ivan
Djordjevic, School of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences, University of Texas Rio
Grande Valley, 1201 West University Drive, Edinburg, TX 78539-2999, USA
(ivan.djordjevic.us@gmail.com), Valerie Manzano, School of Mathematical and
Statistical Sciences, University of Texas Rio Grande Valley, 1201 West University
Drive, Edinburg, TX 78539-2999, USA (vmdance94@gmail.com), Sergio Soto
Quintero, School of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences, University of Texas Rio
Grande Valley, 1201 West University Drive, Edinburg, TX 78539-2999, USA
(ssoto14@stedwards.edu), Mrinal Kanti Roychowdhury, School of Mathematical and
Statistical Sciences, University of Texas Rio Grande Valley, 1201 West University Drive,
Edinburg, TX 78539-2999, USA (mrinal.roychowdhury@utrgv.edu), and Hilda
Tejeda, School of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences, University of Texas Rio
Grande Valley, 1201 West University Drive, Edinburg, TX 78539-2999, USA
(sophia.tejeda.06@gmail.com).
Quantization for the mixtures of overlap probability distributions, pp. 31–54.
ABSTRACT. Optimal quantization for mixed distributions has emerged as a compelling
area of study. In this work, we have focused on a mixed distribution formed from
two uniform distributions with partially overlapping supports. For this class of
distributions, we have examined the structure of optimal sets of 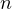 -means and the
corresponding
-means and the
corresponding 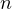 th quantization errors for all positive integers
th quantization errors for all positive integers 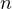 . Initially, we
explicitly determined the optimal sets and quantization errors for
. Initially, we
explicitly determined the optimal sets and quantization errors for 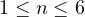 .
Subsequently, we established several key lemmas and propositions and proposed an
algorithm that facilitates the computation of optimal
.
Subsequently, we established several key lemmas and propositions and proposed an
algorithm that facilitates the computation of optimal 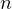 -means and quantization
errors for all
-means and quantization
errors for all 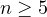 . Numerical results are also presented to illustrate the
application of the algorithm in deriving these quantities. The findings of this
study offer valuable insight and serve as a foundation for further research on
quantization in the context of mixed distributions with overlapping supports.
. Numerical results are also presented to illustrate the
application of the algorithm in deriving these quantities. The findings of this
study offer valuable insight and serve as a foundation for further research on
quantization in the context of mixed distributions with overlapping supports.
Shichuang Wang, Department of Mathematics and Statistics, North China University
of Water Resources and Electric Power, Jinshui E Road, Zhengzhou, Henan, 450046, P.
R. China; Institute of Mathematics, Henan Academy of Sciences, Zhengzhou, Henan
450046, P. R. China (x20231080769@stu.ncwu.edu.cn), and Feng Zhao, Department of
Mathematics and Statistics, North China University of Water Resources and Electric
Power, Jinshui E Road, Zhengzhou, Henan, 450046, P. R. China;Institute of
Mathematics, Henan Academy of Sciences, Zhengzhou, Henan 450046, P. R. China
(zhaofeng@ncwu.edu.cn).
The mean value estimate for Fourier coefficients of automorphic forms, pp.
55–69.
ABSTRACT. Let f be a normalized holomorphic cusp form of even integral weight k for
the full modular group Γ = SL(2, ℤ). In this paper, we investigate the mean value
estimate of higher moments of Fourier coefficients λf⊗ ⊗lf(n) of the l-fold product of f.
⊗lf(n) of the l-fold product of f.
Guodong Hua, School of Mathematics and Statistics, Weinan Normal University,
Weinan, Shaaxi Province, China 714099, Research Institute of Qindong
Mathematics, Weinan Normal University, Weinan, Shaaxi Province, China 714099
(gdhuasdu@163.com).
The distributions of Fourier coefficients associated to multiple cusp forms on arithmetic
progressions, pp. 71–93.
ABSTRACT. Let f and g be two distinct normalized primitive holomorphic cusp forms
of even integral weights k1 and k2 for the full modular group Γ = SL(2, ℤ), respectively.
And denote by λf(n) and λg(n) the nth normalized Fourier coefficients of f and g,
respectively. In this paper, we are interested in the average behaviour of the following
sum
where i,j ≥ 1 are positive integers, and q is a prime with (ℓ,q) = 1.
Huafeng Liu, School of Mathematics and Statistics, Shandong Normal University
Jinan, Shandong 250358, China (huafengliu@sdnu.edu.cn), and Jingyang Lü, School of
Mathematics and Statistics, Shandong Normal University
Jinan, Shandong 250358, China (lvjingyang@sdnu.edu.cn).
On power sums and sign changes of Fourier coefficients of cusp forms, pp. 95–129.
ABSTRACT. Let f be a normalized Hecke eigenform of weight k for the full modular
group SL(2, ℤ). Denote by λf(n) the n-th Fourier coefficient of f. Let Q(x) denote a
primitive integral positive definite binary quadratic form (reduced form) given by
Q(x) = ax12 + bx1x2 + cx22, where x = (x1,x2) ∈ ℤ2,a,b,c ∈ ℤ with gcd(a,b,c) = 1 and
fixed discriminant D = b2 − 4ac < 0. We assume that for such discriminant D, the class
number h(D) is 1. In this paper, we first establish the asymptotic formulae for the sums
of Fourier coefficient λf(n) supported on the integers n represented in the form of Q(x).
Moreover, we show a quantitative result for the number of sign changes of the
sequence of Fourier coefficients λf(n) with n represented in the form of Q(x) in the
interval (x,2x] for sufficiently large x. Our results improve previous results.
Raju Biswas, Department of Mathematics, Raiganj University, Raiganj, West
Bengal 733134, India (rajubiswasjanu02@gmail.com), and Rajib Mandal,
Department of Mathematics, Raiganj University, Raiganj, West Bengal 733134, India
(rajibmathresearch@gmail.com).
Solutions of systems of certain Fermat-type PDDEs, pp. 131–162.
ABSTRACT. The objective of this paper is to investigate the existence and the forms of
the pair of finite order entire and meromorphic solutions of some certain systems of
Fermat-type partial differential-difference equations of several complex variables. These
results represent some refinements and generalizations of the earlier findings, especially
the results due to Xu et al. (J. Math. Anal. Appl. 483(2) (2020)). We provide some
examples to support the results.
Lei Mou, School of Mathematical Sciences, Capital Normal University, Beijing 100048,
China (moulei@cnu.edu.cn), and Piyu Li, School of Mathematics and Statistics, Xuzhou
University of Technology, Xuzhou 221018, China (lpy91132006@aliyun.com.cn).
Star countability of infinite products of subspaces of ordinals, pp. 163–172.
ABSTRACT. For an infinite cardinal κ, a topological space X is called κ-compact if
every F ⊆ X with |F|≥ κ has an accumulation point. A space X is said to
be star countable (respectively, star Lindel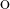 f) if for every open cover 𝒰 of X,
there exists a countable subset (respectively, a Lindel
f) if for every open cover 𝒰 of X,
there exists a countable subset (respectively, a Lindel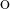 f subspace) F of X such
that St(F,𝒰) = X. For each i < ω, let Ai be a subspace of an ordinal. We give
a characterization when ∏
i<ωAi is κ-compact, where κ > ω is regular. We
show that the three conditions of ∏
i<ωAi being ω1-compact, star countable
and star Lindel
f subspace) F of X such
that St(F,𝒰) = X. For each i < ω, let Ai be a subspace of an ordinal. We give
a characterization when ∏
i<ωAi is κ-compact, where κ > ω is regular. We
show that the three conditions of ∏
i<ωAi being ω1-compact, star countable
and star Lindel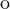 f are equivalent. We also prove that for each ordinal λ with
cf(λ) = ω and λ > ω1, the product λω1 is star Lindel
f are equivalent. We also prove that for each ordinal λ with
cf(λ) = ω and λ > ω1, the product λω1 is star Lindel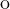 f but not star countable.
f but not star countable.
Attila Losonczi, Budapest Semesters in Mathematics College International, Hungary
1406 Budapest Bethlen Gábor tér 2 (alosonczi2@gmail.com).
On the cardinality of π(δ), pp. 173–180.
ABSTRACT. We prove that the cardinality of transitive quasi-uniformities
in a quasi-proximity class is at least 22ℵ0
if there exist at least two transitive
quasi-uniformities in the class. The transitive elements of π(δ) are characterized if 𝒱δ is
transitive, and in this case we give a condition when there exists a unique transitive
quasi-uniformity in π(δ).
Earnest Akofor, Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, Faculty of
Science, University of Bamenda, PO Box 39 Bambili, NW Region, Cameroon
(eakofor@gmail.com).
Modulo arithmetic of function spaces: Subset hyperspaces as quotients of function
spaces, pp. 181–207.
ABSTRACT. Let X be a (topological) space and Cl(X) the collection of nonempty
closed subsets of X. Given a topology on Cl(X), making Cl(X) a space, a (subset)
hyperspace of X is a subspace of Cl(X) into which X is embedded by mapping each point
to its singleton. In this note, we characterize certain hyperspaces of X as explicit quotient
spaces of X-valued function spaces and discuss metrization of associated compact-subset
hyperspaces in this setting. In particular, we find that any hyperspace topology
containing the Vietoris topology is a quotient of a function space topology containing the
topology of pointwise convergence.
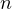 -means and the
corresponding
-means and the
corresponding 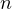 th quantization errors for all positive integers
th quantization errors for all positive integers 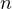 . Initially, we
explicitly determined the optimal sets and quantization errors for
. Initially, we
explicitly determined the optimal sets and quantization errors for 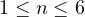 .
Subsequently, we established several key lemmas and propositions and proposed an
algorithm that facilitates the computation of optimal
.
Subsequently, we established several key lemmas and propositions and proposed an
algorithm that facilitates the computation of optimal 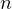 -means and quantization
errors for all
-means and quantization
errors for all 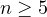 . Numerical results are also presented to illustrate the
application of the algorithm in deriving these quantities. The findings of this
study offer valuable insight and serve as a foundation for further research on
quantization in the context of mixed distributions with overlapping supports.
. Numerical results are also presented to illustrate the
application of the algorithm in deriving these quantities. The findings of this
study offer valuable insight and serve as a foundation for further research on
quantization in the context of mixed distributions with overlapping supports.

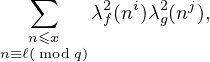
 f) if for every open cover
f) if for every open cover  f subspace)
f subspace)  f are equivalent. We also prove that for each ordinal
f are equivalent. We also prove that for each ordinal  f but not star countable.
f but not star countable.